The term structure of VIX how the price of future contracts relates to the spot is normally in contango upward sloping meaning that VIX futures have a higher price than the spot. The unconditional upward slope is strengthened when the frequency of recession periods in the data isadjustedtomatchthehistoricaloccurrenceofrecessions.

If the VIX is upward-sloping it implies that investors expect to see the.
Why is volatility term structure upward sloping. Since volatility is a measure of systematic risk the VIX term structure suggests the trend of future market risk. If the VIX is upward-sloping it implies that investors expect to see the. The upward sloping nature of the curve suggests that market participants believe volatility will increase from 13 in the future which makes sense because the long-term average VIX level is around 20.
The term structure of volatility can have a downward slope with higher volatilities skewing to the near-term option strike dates or an upward slope if higher volatilities are found in. The term structure of the VIX index is the VIX plotted on different expirations. It suggests the markets expectation on the future volatility.
Since volatility is a measure of systematic risk the. The term structure of VIX how the price of future contracts relates to the spot is normally in contango upward sloping meaning that VIX futures have a higher price than the spot. This means that the futures market is pricing on average than volatility will rise from current levels.
Historically this premium to spot has been too high relative to the subsequent realized volatility and thus traders have. The term structure of yield volatility is the relationship between the volatility of bond yields-to-maturity and times-to-maturity. The term structure of bond yields also called the term structure of interest rates is typically upward sloping.
However it can be different depending on some factors including government policy. In the simplest case this explains why an upward sloping SP 500 curve translates into an upward sloping VIX futures curve. But there is more.
Sloping term structures of risk premium and volatility of dividend strips and an upward-sloping yield curve. We emphasize that the shape of the model-implied term structures depends mainly on the preference parameters and the sign of the correlation between shocks to contemporaneous output growth and shocks to expected output growth. When this correlation is negative a negative consumption.
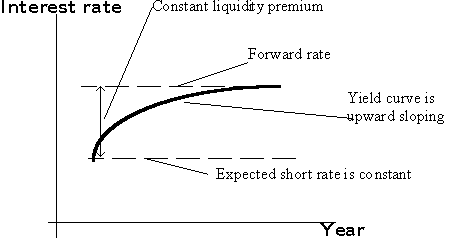
Financial Economics Term Structure Upward-Sloping Yield Curve A widespread point of view is that investors tend to have a short-time horizon and that bond issuers have a long time-horizon. Then market equilibrium requires R 2 1 2 R 1 E R 1. Otherwise investors would buy only one-year bonds and bond issuers would issue only two-year bonds which would be inconsistent with market.
The term of the structure of interest rates has three primary shapes. Upward slopinglong-term yields are higher than short-term yields. This is considered to be the normal slope of the yield.
First the term-structure of consumption volatility is upward-sloping whereas that of dividend volatility is downward-sloping Marf e2013. The former occurs because the con- sumptions speed of recovery is not high enough to outweigh time-varying risk of disasters and 2Consistent with the international evidence documented byGourio2008 our calibration implies that dividends recover. We show that the term structure of equity risk premia in the strip data is conditionally upward sloping in expansions downward sloping in recessions and unconditionally upward sloping.
The unconditional upward slope is strengthened when the frequency of recession periods in the data isadjustedtomatchthehistoricaloccurrenceofrecessions. An upward-sloping term structure is a natural byproduct of a bullish market and thats all there is to it. Yes eventually at the end of the bullish market phase the term structure will be predicting an increase in volatility but what about all the other days during the bull market when it was in the same state but the market just kept going higher.
As with any of the volatility indicators it is a. The model indicates that a downward sloping volatility term structure corresponds to a potential long disaster and an upward sloping volatility term structure corresponds to a potential short disaster. Stocks with high sensitivities to the VIXslope have high loadings on the disaster duration risk thus earn higher risk premium.
So why is this underperformance happening. One of the problems with this type of strategy is that volatility in general can and does sometimes rise even when the VIX futures term structure remains upward sloping and in contango. There are many examples of this since the inception of these volatility ETPs.
One of the more pronounced was in 2012. Heres the VIX index nearly doubling in a three. Term structure of interest rates is upward-sloping when accounting for recoveries and downward-sloping otherwise.
The model quantitatively reconciles a high equity pre- mium and a low risk-free rate with the shape of the term structures which are at odds in other models. Recoveries Time-Varying Rare Disasters Term Structures of Equity Volatility and Risk Premia JEL Classi cation. When implied volatility is plotted against strike price the resulting graph is typically downward sloping for equity markets or valley-shaped for currency markets.
For markets where the graph is downward sloping such as for equity options the term volatility skew is often used. The normal yield curve is a yield curve in which short-term debt instruments have a lower yield than long-term debt instruments of the same credit. Yield curves are usually upward sloping asymptotically.
The longer the maturity the higher the yield with diminishing marginal increases that is as one moves to the right the curve flattens out. There are two common explanations for upward sloping yield curves. First it may be that the market is anticipating a rise in the risk-free rate.
If investors hold off investing now they may receive a better rate in the future.