Viz reproduction excretion metabolism and response to stimuli. 9 The cell cycle of a eukaryotic unicell such as the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe consists of a growth phase G1 a phase of DNA synthesis S a second growth phase G2 and mitosis itself M repeated ad infinitum Figure 223.

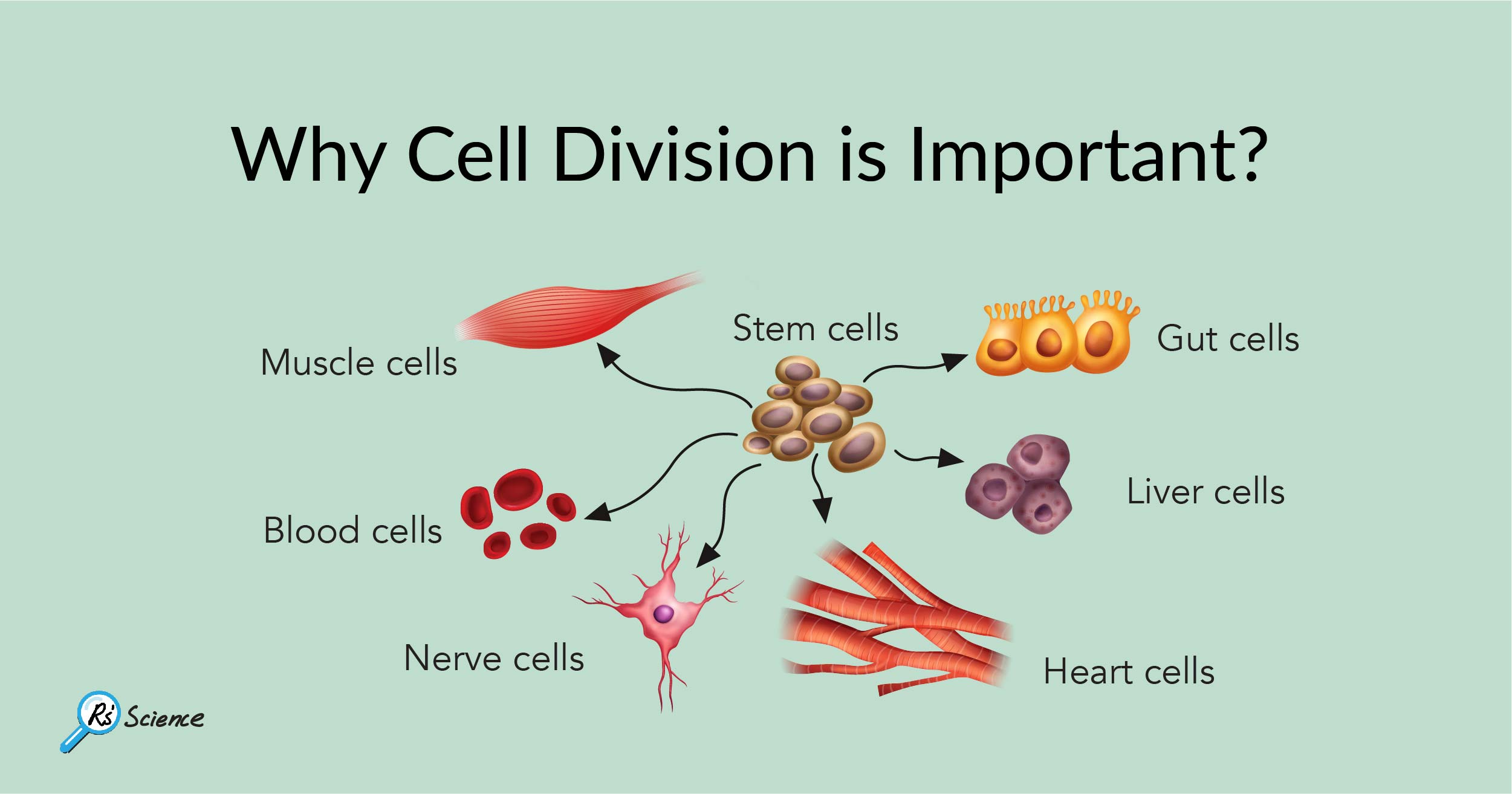
Multicellular organisms need cell division to grow and to replace dead or damaged cells and unicellular cell division is the only way single-celled organisms can reproduce.
Why is the cell cycle important to unicellular organisms. The cell cycle is important because it helps cells to sustain their lives marinodiasmd marinodiasmd 03032015 Chemistry Middle School How is the cell cycle important to some unicellular organisms. 1 See answer marinodiasmd is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points.
The three main reasons why cell division is important in organisms are reproduction repair and growth according to McDougal Littell Science Cells and Heredity Cell division is necessary in order for life to continue. Cell division serves as a means of reproduction in unicellular organisms through binary fission. The Cell Cycle In unicellular organisms division of one cell reproduces the entire organism.
Multicellular organisms depend on cell division for. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell division is an integral part of the cell cycle the life of a cell from formation to its own division. In unicellular organisms cell proliferation is the default behaviour and its rate is limited only by the availability of energy and raw materials.
9 The cell cycle of a eukaryotic unicell such as the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe consists of a growth phase G1 a phase of DNA synthesis S a second growth phase G2 and mitosis itself M repeated ad infinitum Figure 223. AnswerMitosis plays an important part in the life cycle of most living thingsExplanationMitosis plays an important part in the life cycle of most living thing kimoclash2008 kimoclash2008 11232020 Biology High School Why is mitosis important to unicellular organisms. Why is the so-called resting stage the interphaseconsidered the most active stage of cell cycle.
Why is the cell cycle important in multicellular organisms it increases the size of the organism During which phase of mitosis do the sister chromatids in each chromosome. Why is cell division important for both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms need cell division to grow and to replace dead or damaged cells and unicellular cell division is the only way single-celled organisms can reproduce.
Why does cell division remain important to an adult organism even after it is fully developed. Cell division is important for unicellular and multicellular organisms because it allows for growth development and reproduction of living organisms. The unicellular organism is an integrated living organism that proves that the cell is the unit of structure and function because it has the ability to do all its biological functions.
There are a lot of unicellular micro-organisms around us that can not be seen by the naked eye as the bacteria and the yeast fungus Some unicellular organisms are harmful and others are useful. Solution for What is the importance of cell cycle to an organism. Organisms use cell division for growth and the maintenance and repair of cells and tissues.
Single-celled organisms use cell division as their method of reproductio view the full answer. This phenomenon plays a major role in developmental pathways 1 provides a homeostatic balance of cell populations and is deregulated in many diseases including cancer. Control of cell number is determined by an intricate balance of cell death and cell proliferation.
Accumulation of cells through suppression of death can contribute to cancer and to persistent viral infections while excessive death. In multicellular organisms such as yourself cell-cell signaling allows cells to coordinate their activities ensuring that tissues organs and organ systems function correctly. Does that mean that unicellular organisms like yeast and bacteria dont use cell-cell signaling pathways.
True unicellular organisms like the bacteria or protists function as individual organisms in their ecological niche. They exhibit the characteristics of life as displayed by multicellular organisms. Viz reproduction excretion metabolism and response to stimuli.
However the most pertinent difference being that a single cell from a multicellular organism cannot survive in the wild on its own. It needs help from the.