
Wound Type Rotor or Slip Ring Type Rotor. Rotor as the name suggests it is a rotating part of an electrical machine in which current is induced by transformer action from rotating magnetic field.
Rotor as the name suggests it is a rotating part of an electrical machine in which current is induced by transformer action from rotating magnetic field.
Rotor current frequency in induction motor. The frequency of rotor current in an induction motor. The frequency of the rotor current fr Ns x P120 so fr 0 if the slip is zero. If the operating speed is zero Ns N and the frequency of the rotor current is the same as the frequency of the stator current.
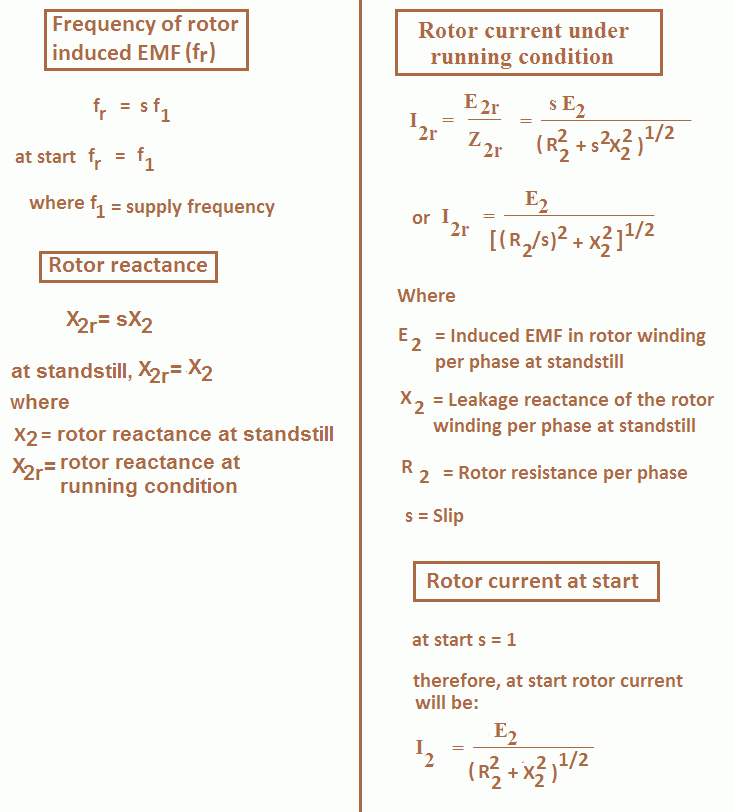
F source frequency in Hz. The frequency fr of the rotor current in an induction motor is given by the expression fr s. F s slip f supply frequency.
Frequency of the rotor current. Lets say a three-phase induction motor is rated 50HP 480V 60Hz and 1150 RPM. Is developed torque mean initial powers torque.
The frequency of the rotor current fr Ns x P120 so fr 0 if the slip is zero. If the operating speed is zero Ns N and the frequency of the rotor current is. The frequency of the rotor current fr Ns x P120 so fr 0 if the slip is zero.
If the operating speed is zero Ns N and the frequency of the rotor current is the same as the frequency of the stator current. F source frequency in Hz. You mean rotor frequency in an induction motor.
It is the frequency of alternating current flowing in rotor winding. Rotor frequency slip supply frequency. Therefore at standstill slip 1 rotor frequency is equal to supply frequency.
As motor picks up speed slip becomes less than one. And rotor frequency gets lesser than supply frequency. E 2 standstill rotor induced emfphase X 2 standstill rotor reactancephase f 2 rotor current frequency at standstill When rotor is stationary ie.
S 1 the frequency of rotor emf. Is the same as that of the stator supply frequency. Rotor as the name suggests it is a rotating part of an electrical machine in which current is induced by transformer action from rotating magnetic field.
Induction motor rotor is of two types. Wound Type Rotor or Slip Ring Type Rotor. The speed of the induction motor is.
Nr120fP 1-s With an increase in frequency the speed of the rotating magnetic field gets increased and the speed of the motor increase. If the motor is to deliver the same torque at the increased speed the torque of the motor gets reduced. Frequency of Rotor Current When the rotor is stationary the frequency of rotor current is the same as the supply frequency.
But when the rotor starts revolving then the frequency depends upon the relative speed or on slip- speed. Let at any slip-speed the frequency of the rotor current be f. An induction motor consists essentially of two main parts.
A a stator and b a rotor. A Stator The stator of an induction motor is in principle the same as that of a synchronous motor or generator. It is made up of a number of stampings which are slotted to receive the windings Fig342 a.
The motor parameters of Induction Motors are crucial when the Field Oriented Control Close loop torquespeed control is needed. More specifically the rotors flux absolute position is determined mathematically using known speed voltage and current and a model representation of the motors main parameters shown in the figure below. In an induction motor the relation between synchronous speed supply frequency and the number of stator poles is given by When the rotor rotates at a speed N then the rotor conductor cut the rotating magnetic field at the relative speed ie N s - N.
The frequency of the rotor induced emf or current f r can be expressed as. In a high frequency induction motor EMF is induced leading to current flow. Torque in the rotor coil increases.
As frequency increases Impedance of the Rotor. Rotor Current and Power Factor R2 Rotor resistance per ph under standstill condition X2 Rotor reactance per ph under standstill condition In running condition Rotor impedance per phase Kongunadu college of Engineering Technology Three phase Induction Frequency Rotor EMF Current and Power factor related Problems. The speed of the rotor during starting condition is zero therefore the relative speed between stator rotating magnetic field and rotor speed is Ns N Ns When the rotor conductors cut the rotating magnetic field an emf will be induced in it.
Let us consider that the induced emf in the rotor is E2. The rotor and stator are separated by an air gap which allows free rotation of the rotor. Typical Induction Motor Rotors The magnetic field generated in the stator induces an EMF in the rotor bars.
In turn a current is produced in the rotor bars and shorting ring and another magnetic field is. Induction Motor 4 - Electrical frequency at the Rotor. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device.
Up next in 8. Introduction to Induction Motor The alternating current motor that used the phenomena of the electromagnetic induction to produce the current and flux in the rotor to produce torque is recognized as the induction motor. It is also is known as the asynchronous motor.