Consequences of the behavior Operant Behavior Operant behavior The consequences that follow a certain response affect the future probability or strength of the response Press Lever Food Press Lever Shock Operant behaviors are elicited by the organism voluntary Operant behavior defined as a class of response eg class. Answer According to Skinner the functional analysis of behavior should be done in the context of two observable things-the operator is defined as a specific observable behavior and result which is.
/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)
Operant conditioning was defined and studied by behavioral psychologist BF.
Operant behaviors are usually defined as a. Operant behavior is a term first used by BF. Skinner who was one of the best-known psychologists in the behaviorism school. In his many years of work Skinner theorized that organisms were often influenced in behavior by consequences and that previous consequences would have an affect on future behavior.
Consequences could be either natural or contrived and were often contrived in the types of studies on operant behavior. Operant behavior is that which is said to meet two conditions. 1 It is freely emitted by an animal in the sense that there is no obvious triggering stimulus.
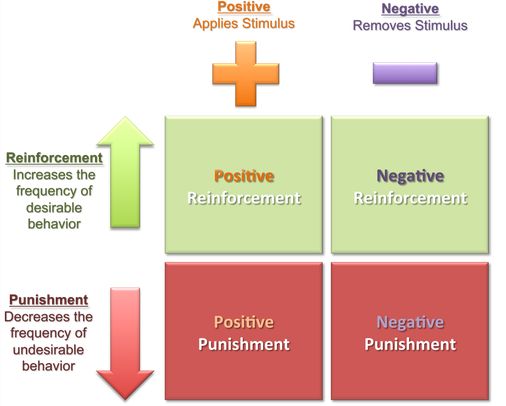
2 It is susceptible to reinforcement and punishment by its consequences such that it can be caused to go up or down in frequency respectively. Operant behavior which goes along with operant conditioning refers to behavior that operates on the environment or is controllable by the individual. Operant behavior is done because it produces some type of consequence.
The behavior is operant response since its existence results in a particular consequence which affects the eventual possibility of that response. As compared to the behaviors which are conditioned classically also termed as elicited by stimuli the operant behaviors are emitted by the organism. This is used to signal that operant behavior has more.
Operant behaviors are usually defined as a a class of behaviors that are topographically similard operant and respondent D 228 MD 53. Operant Conditioning class of behaviors that lead to. Operants themselves consist of actions that are performed on the environment that produce some consequence.
Operant behaviors that bring about reinforcing environmental changes ie if they provide some reward to the individual or eliminate an aversive stimuli are likely to be repeated. In the absence of reinforcement operants are weakened. A class of emitted responses that result in certain consequences.
These consequences in turn affect the future probability or strength of those responses. A type of learning in which the future probability of a behavior is affected by its consequences. By Team Guffo Published 2019 Updated 2020.
Answer According to Skinner the functional analysis of behavior should be done in the context of two observable things-the operator is defined as a specific observable behavior and result which is. Consequences of the behavior Operant Behavior Operant behavior The consequences that follow a certain response affect the future probability or strength of the response Press Lever Food Press Lever Shock Operant behaviors are elicited by the organism voluntary Operant behavior defined as a class of response eg class. Operant conditioning is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment.
In operant conditioning behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on the consequences of that behavior. Operant conditioning was defined and studied by behavioral psychologist BF. Behaviors that are voluntary in nature rather than reflexive are usually associated with operant conditioning.
Applied behavior analysis may be defined as the process of applying behavioral principles to improve behaviors while simultaneously evaluating whether noted changes may be attributed to the application of those principles. Simply describe the behavior in terms of its outcome. The bug finds the food.
Behavior guided by its consequences was called by Skinner operant behavior and the term has become generally accepted. The word operant refers to an essential property of goal-directed behavior. That it have some effect on the environment.
If the bacterium cannot move or. Operant behavior is said to be voluntary. The responses are under the control of the organism and are operants.
For example the child may face a choice between opening the box and petting a puppy. In contrast classical conditioning involves involuntary behavior based on the pairing of stimuli with biologically significant events. Tact a verbal operant that is under the antecedent control of a non-verbal stimulus and is followed by generalized conditioned social reinforcement.
Echoic a verbal operant that is under the antecedent control of a prior vocal stimulus and is followed by GCSR point-to. Consequences that result in an increase or decrease the frequency in the same type of behavior under similar conditions. Operant behaviors are controlled by their consequences.
Example in everyday context. Your cell phone lights up and you see a text from an acquaintance. You respond to the text message.
In the laboratory establishing operations usually involve a history of deprivation for some event that functions as primary reinforcement eg food. Most human behavior however is regulated by conditioned reinforcement. To investigate the manding of conditioned reinforcement Michael 1988 suggested the use of a conditioned establishing operation CEO.
The procedure is called the blocked-response CEO in which a response that usually.