
Profit Maximization Problem A closer look at marginal revenue. These examples show you that you should always consider if your short-term profit maximization will be in support of your long-term sustainable goals.
It is mainly a short-term goal and is primarily restricted to the accounting analysis of the financial year.
Negative effects of profit maximization. What Are Some Disadvantages of Profit Maximization. Some of the disadvantages that can result from a company becoming overly focused on profit maximization are the ignoring of risk factors a lessening or loss of transparency and the compromising of ethics and good business practices. Disadvantages of Profit MaximizationAttack on Profit Maximization.
Ambiguity in the Concept of Profit. It has been pointed out that in the assumption of profit maximization. The concept of profit has never been unambiguously stated.
Is it rate of profit total or net profits that a firm tends to maximize. The three concepts have entirely different implications for price theory. Profit maximization can also conflict with a customer-centric approach which means companies may mislead customers to generate revenue.
Lack of transparency can damage long-term goodwill with customers which can have dire financial consequences in the future. While profit maximization in financial management has the potential to bring in extra money in the short-term long-term earning could be drastically diminished. Lowering production quality for the sake of increased profits will hurt your brand upset customers and allow competitors to steal your business.
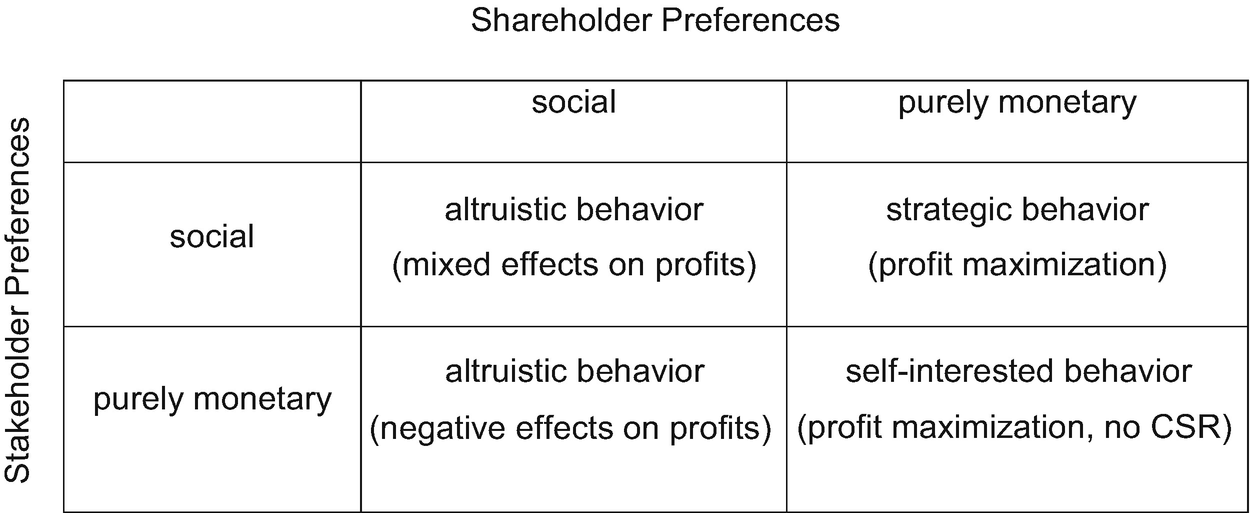
For instance if your organization decides to unload all available inventory to a. However unlimited profit maximization cannot be defended by any reasonable ethical theory. The idea that corporations should pursue the interests of their shareholders takes its starkest form in the sentiment expressed by Milton Friedman that the social responsibility of business is to increase its profits Friedman 1970.
Friedman is very clear in stating that it is illegitimate for a corporation to act in a way that is detrimental to shareholder returns. There are significant problems the world is facing income disparities environmental concerns human trafficking and many claim that profit seeking businesses are not only not helping they are exacerbating some of these problems. Social enterprises that do not maximize profits are seen as the solution.
We begin by considering alternatives to profit maximization in a free. A firm may be able to maximize its revenue in a way that does not make for profit maximization. For instance managers could step up their advertising efforts.
While this might hike up sales and lead to additional revenue the deduction of advertising costs from the revenues means that profits will be reduced. The process of increasing the profit earning capability of the company is referred to as Profit Maximization. It is mainly a short-term goal and is primarily restricted to the accounting analysis of the financial year.
It ignores the risk and avoids the time value of money. It is primarily concerned as to how the company will survive and grow in the existing competitive business environment. All of the correlations between competitor-oriented objectives and profits were negative ranging from minus 028 to minus 073 according to Armstrong and Green.
It ignores the time value of money. Profit maximization does not consider the risk of the business concern. Risks may be internal or external which will affect the overall operation of.
There would be no effect on the total revenue curve or the shape of the total cost curve. Consequently the profit maximizing point would remain the same. This point can also be illustrated using the diagram for the marginal revenuemarginal cost perspective.
A change in fixed cost would have no effect on the position or shape of these curves. Nowadays many large multinational corporations which occupy increasing shares in the market and high statues in the society are usually powerful in having both positive and negative effects on the public to a great extent. As a consequence today the concept of Corporate Social Responsibilities CSR draws much more public attention.
Social responsibility goes beyond profit making and social obligation. CSR is a business intention focusing on minimizing the harmful effects. Profit Maximization Problem A closer look at marginal revenue.
When monopolist increases output by 1 unit this additional unit produces 2 effects on firms revenue. If the firm sells 1 more unit it earns and the firms revenue increases. When offering 1 more unit the firm needs to.
Profit maximization arises with regards to an input when the value of the marginal product is equal to the input cost. A second characteristic of a maximum is that the second derivative is negative or nonpositive. This property is known as the second-order condition.
These examples show you that you should always consider if your short-term profit maximization will be in support of your long-term sustainable goals. Quality of the Product or Service. Another limitation of solely relying on the theory of profit maximization is the potential to decrease the quality of your product or service.
If you are focused exclusively on profits you are more likely to use. Corporate Social Responsibility versus Profit Maximization Introduction Nowadays many large multinational corporations which occupy increasing shares in the market and high statues in the society are usually powerful in having both positive and negative effects on the public to a great extent. As a consequence today the concept of Corporate Social Responsibilities CSR draws much more public attention.
Social responsibility goes beyond profit. Schumpeterian theory derives innovation and imitation behavior endogenously from the profit-maximization problem facing a prospective innovator It assumes that faster growth implies a higher rate of firm turnover because this process of creative destruction allows new innovators to enter the market and for former innovators to exit. The Schumpeterian perspective recognizes the heterogeneity of.
Interestingly introduction of TPR has a negative but insignificant effect on reported profits by MNCs in the high-tax countries which may reflect the two offsetting effects of TPR on the tax base. However the effect on reported profits by MNCs in the low-tax countries is also negative but three times larger and highly significant. The results therefore suggest that the overall effect of TPR on the corporate tax base and total revenue is asymmetric.