Electrostatic loudspeakers can be augmented with separate dynamic woofers or a subwoofer to extend the low-frequency response and provide some dynamic impact. On the plus side the near-field approach tends to be valid over a wider frequency range.

Loudspeaker designers generally try for flat on-axis response by tailoring the crossover to compensate for this drop in frequency response.
Loudspeaker low frequency response. Advertentie Geniet van een ruime selectie producten van de grootste merken. Snelle levering Wij verkopen alles binnen electronica. Vind alles wat je nodig hebt.
Both techniques described in this article produce reliable estimates of loudspeaker low-frequency response in the absence of an anechoic chamber. Both techniques agree reasonably well given their different approaches to the problem. On the plus side the near-field approach tends to be valid over a wider frequency range.
Frequencies causing the on-axis response to fall by as much as 6dB in this frequency range. Loudspeaker designers generally try for flat on-axis response by tailoring the crossover to compensate for this drop in frequency response. If a speaker designed this way is now tested in a half-space it will show a rise in low-frequency response.
As long as you know the amplitude tolerance - 3dB the frequency response range or width tells you how high or low the speaker goes. A speaker rated as 20Hz 25kHz - 3dB will play lower bass and higher treble sounds than a speaker that measures 40Hz 20kHz - 3dB. Low frequency cutoff 343 2 x 2 h 2 05 Where 343 ms -1 is the speed of sound.
For a room with a ceiling height of 24 m and a measuring distance of 1 m this gives. Low frequency cutoff 343 2 05 2 12 2 05 132 Hz. Frequencies lower than 20 Hz are beyond our frequency hearing range.
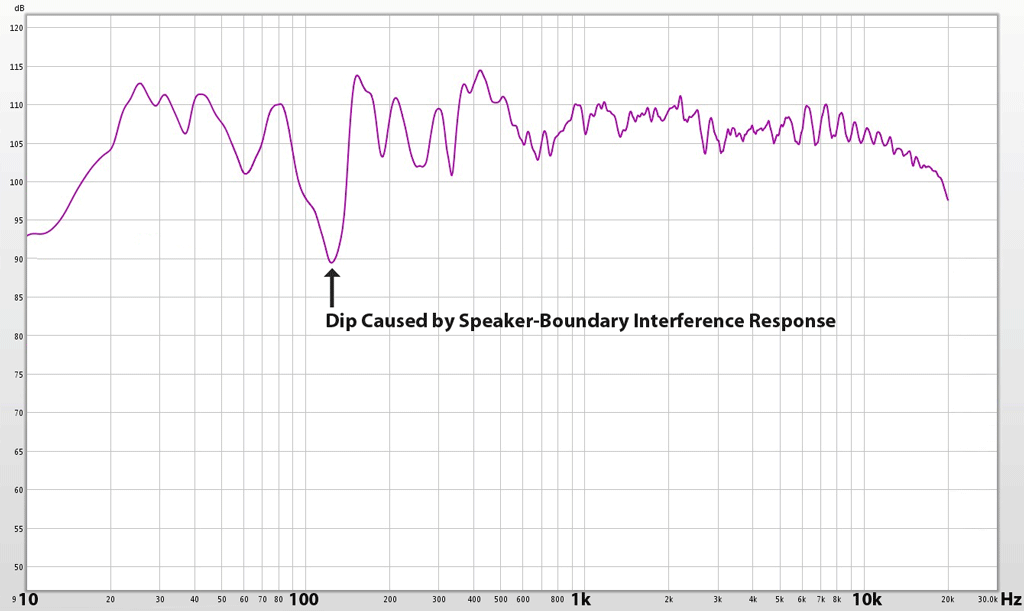
Our low frequency response test - which starts as low as 10 Hz - should remain inaudible until it reaches 20 Hz. If you hear frequencies below 20 Hz suspect this test to be corrupted by Harmonic Distortion generated from your speaker or. Below resonance the port and speaker radiation are out of phase so they add destructively giving less bass than a closed box At the resonant frequency the port response much greater than the speaker response because the back load presented to the loudspeaker is maximum at the resonance of the port.
We have seen that the single best predictor of loudspeaker listener preference is frequency response. There are four elements to frequency response. On-axis response listening window response early reflection response and finally power response.
The last two require that you also examine polar response. Anechoic frequency response 6dB. Anechoic frequency response 3dB.
Anechoic linearity deviation between 100Hz and 10kHz. The first two specifications show the frequency extension at high and low frequencies and the last shows how flat the loudspeaker is in the middle ie. Away from the frequency extremes.
Electrostatic loudspeakers can be augmented with separate dynamic woofers or a subwoofer to extend the low-frequency response and provide some dynamic impact. Other electrostatics achieve the same result in a more convenient package. Dynamic woofers in enclosures mated to the electrostatic panels.
The common way of specifying a speakers low-frequency extension is to cite the frequency at which its response is attenuated by 3dB -3dB at 28Hz for example. This method unfairly favors reflex loading because it doesnt take into account the very steep roll-off below the -3dB cut-off frequency. A loudspeaker is typically measured under free-field conditions where sound reflections are highly attenuated such as in an anechoic chamber or outdoors where the reflected signal paths are much longer and thus the reflections much weaker than the direct signal from a speaker andor the impulse response is gated to exclude reflections.
Advertentie Geniet van een ruime selectie producten van de grootste merken. Snelle levering Wij verkopen alles binnen electronica. Vind alles wat je nodig hebt.