It is also a latent heat and is sometimes called the latent heat of fusion. The formula for heat absorbed or liberated by a substance during the change of state.

Latent Heat of Fusion kJmol kJkg Aluminum.
Latent heat of fusion chart. 62 Zeilen Latent Heat of Fusion kJkg Latent Heat of Vaporization kJkg Butter. Oil Palm 35. Latent Heat of Fusion kJmol kJkg Aluminum.
Specific latent heat of fusion kJkg-1 C Specific latent heat of vaporisation kJkg-1 C. The latent heat of fusion is the heat required to convert unit mass 1 kg of substance from solid-state to liquid state at its melting point. The latent heat of ice is 334 X 105 joulekg.
The formula for heat absorbed or liberated by a substance during the change of state. When the state of m kg of solid changes into a liquid at. The specific heat of liquid water is cw 4186 Jkg Co.
The heat of fusion for ice or water is L f 333 x 10 5 Jkg. The specific heat of frozen ice is ci 2090 Jkg Co. Latent heat of fusion also known as enthalpy of fusion is the amount of energy that must be supplied to a solid substance typically in the form of heat in order to trigger a change in its physical state and convert it into a liquid when the pressure of the environment is kept constant.
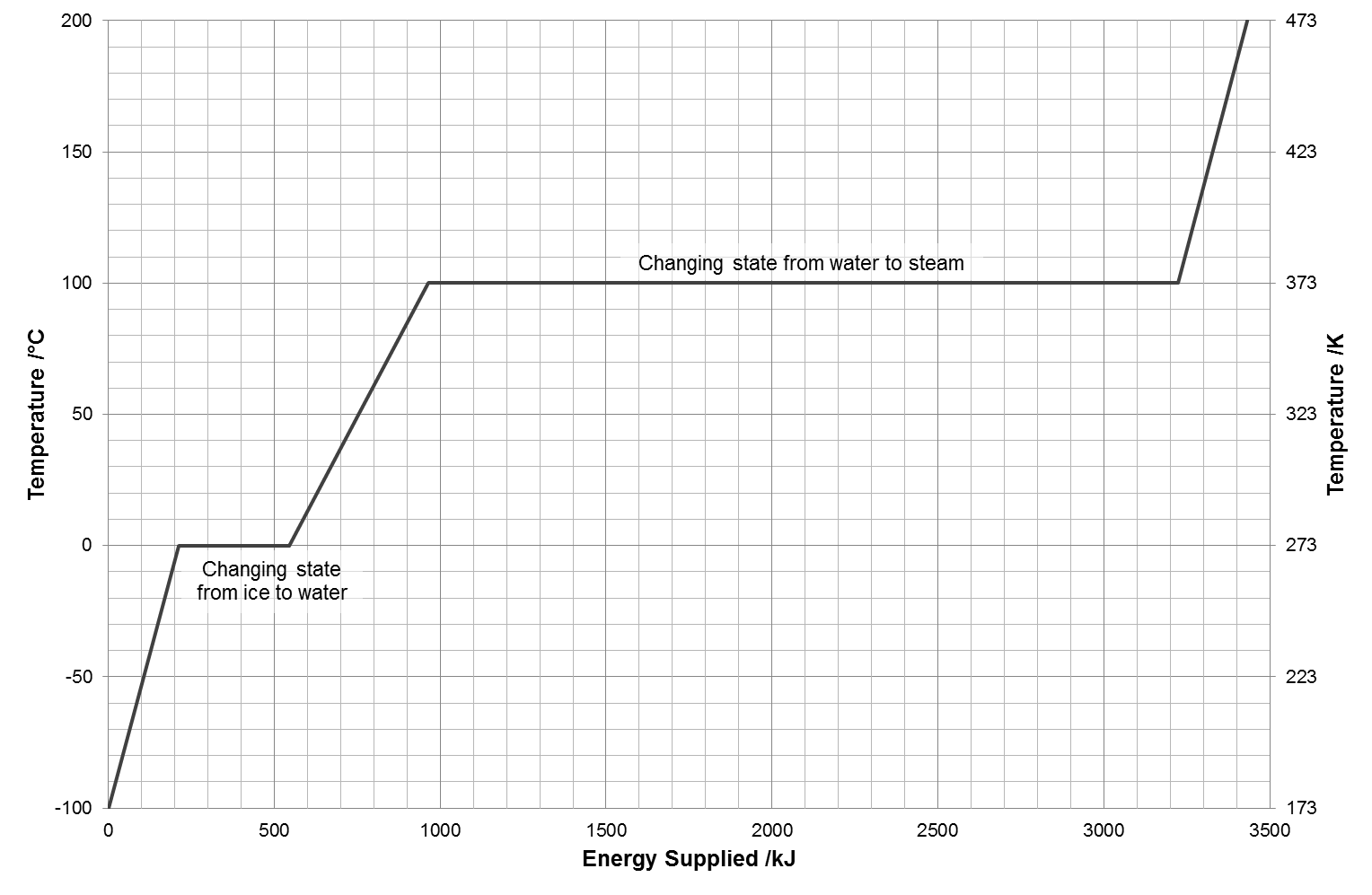
1 33355 Jg heat of fusion of ice 33355 kJkg 33355 kJ for 1 kg of ice to melt PLUS 2 418 JgK 20K 418 kJkgK 20K 836 kJ for 1. Point to the graph to see details or click for full data on that element. The latent heat of fusion of a substance is the amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of the solid into liquid without change in temperature The latent heat of melting for some common solids are indicated below.
1 kJkg 04299 Btulbm 023884 kcalkg. It needs heat energy to melt and so it takes this heat from its surroundings ie. This video shows how the temperature of ice remains at 0C while melting.
Latent heat of fusion is the heat consumed or discharged when matter melts changing stage from solid to fluid-structure at a consistent temperature. The enthalpy of fusion is a latent heat in light of the fact that during softening the heat energy expected to change the substance from solid to fluid at air pressure is the latent heat of fusion as the temperature stays steady during the procedure. Calculate the latent heat of fusion L for each of the three trials you performed.
Assume that the energy lost by the warm water is gained by the ice but notice that the energy is used first to melt the ice then to raise the temperature of the. Example of latent heat of fusion Ice changes at 0 C into water. The latent heat of fusion of ice is 336 10 5 J kg -1.
336 10 5 Joule heat is required to melt 1. The heat of fusion is the quantity of heat necessary to change 1 g of a solid to a liquid with no temperature change Weast 1964 p. It is also a latent heat and is sometimes called the latent heat of fusion.
It has only one value for water because water freezes at one value 0 C and it is 7971 calg or the rounded number 80 calg. Physical model for the latent heat of fusion Jozsef Garai E-mail. Jozsefgaraifiuedu Abstract The induced atomic movement at melting has to overcome on a viscous drag resistance.
It is suggested that the latent heat of fusion supplies the required energy for this physical process. Latent Heat of Fusion Experiment Part 1. 15 points Complete five trials and enter the data be sure to include all units for each experiment into the following chart.
10 points Using the data above and the supplementary sheet calculate the latent heat of fusion for each trial and enter values in the chart above. AnswerLatent heat also known as Heat of Transformation is energy released or absorbed by a body or a thermodynamic system during a constant-temperature pro. 10 points Using the data above and the supplementary sheet calculate the latent heat of fusion for each trial and enter values in the chart above.
10 points In 1-2 paragraphs explain how the lab is performed. This should be written as if you were instructing someone who was not familiar with this lab.