Home study science chemistry organic chemistry organic chemistry solutions manuals A Microscale Approach to Organic Laboratory Techniques 5th edition chapter 42 problem 1Q. Only alkenes and aromatics show a CH stretch slightly higher than 3000 cm -1.
There are a total of 11 protons on the NMR spectrum that can be explained by benzocaine indicating a gain in protons p-aminobenzoic acid would have a total of 7 protons present.
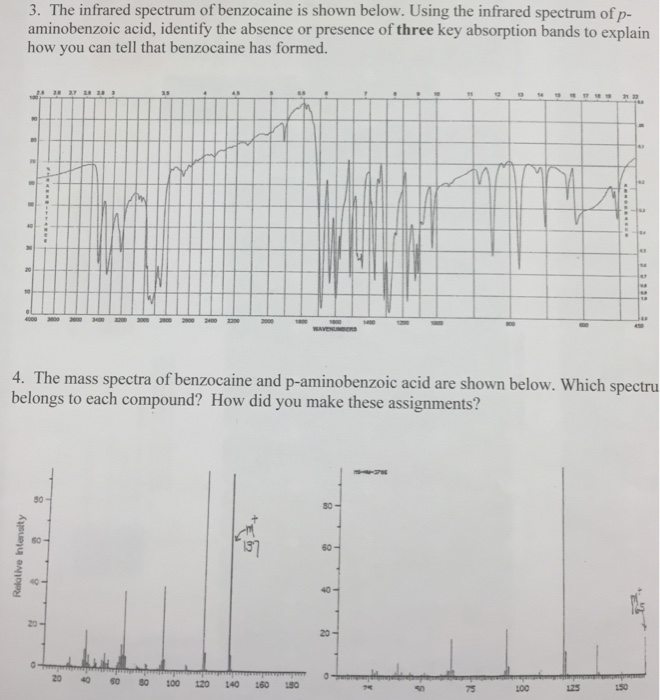
Interpret ir of benzocaine. Benzocaine has the following IR spectrum. And here is its structure. From what I understand.
The two leftmost peaks are the antisymmetrical and symmetrical stretchs of the amine group. Just before the fingerprint region at about 1690 is the carbonyl ester peak and to the right of it also before the fingerprint region is the benzene C-C bonding peaks. The messy broad peaks.
Interpret the infrared and NMR spectra of benzocaine. Home study science chemistry organic chemistry organic chemistry solutions manuals A Microscale Approach to Organic Laboratory Techniques 5th edition chapter 42 problem 1Q. A Microscale Approach to Organic Laboratory Techniques 5th Edition Edit edition.
C 9 H 11 NO 2. Download the identifier in a file. Interpret The IR Spectrum Of Benzocaine.
How Will You Explain The Three N-H Peaks Found In. Interpret The IR Spectrum Of Benzocaine. How Will You Explain The Three N-H Peaks Found In The Spectrum Between 3200 And 3450 Cm-1.
Sample Is Impure And A Carbonyl Peak Is Observed At 1630 Cm-1. Benzoic acid has an IR spectroscopy with large peaks present in the 2500 to 3300 centimeter-1 region in the 1680 to 1750 region in the 1300 region and in the 900 to 1100 region. All of these absorptions coincide with functional groups present in the compound.
The peak noted in the 2500 to 3300 centimeter -1 region is indicative of an OH group. The preparation of benzocaine is a common experiment used in sophomore-level organic chemistry. Its straightforward procedure and predictable good yields make it ideal for the beginning organic student.
Analysis of the product via NMR spectroscopy however can be confusing to the novice interpreter. An inexpensive quick and effective method for simplifying the NMR spectrum is reported. Dimethylacetanilide being intermediate in the synthesis.
Benzocaine or ethyl-4-aminobenzoate was synthesized by Fischer esterification of 4-aminobenzoic acid with absolute ethanol. The intermediates and products were characterized by using infrared IR proton nuclear magnetic resonance 1H. Aldehydes will have similar infra-red spectra to ketones.
The infra-red spectrum for a hydroxy-acid. 2-hydroxypropanoic acid lactic acid This is interesting because it contains two different sorts of O-H bond - the one in the acid and the simple alcohol type in the chain attached to the -COOH group. This is a very useful tool for interpreting IR spectra.
Only alkenes and aromatics show a CH stretch slightly higher than 3000 cm -1. Compounds that do not have a CC bond show CH stretches only below 3000 cm -1. Aromatic hydrocarbons show absorptions in the regions 1600-1585 cm -1 and 1500-1400 cm -1 due to carbon-carbon stretching vibrations in.
Previous Page Next Page. Similar compounds 1-2 of 2 Molid Formula Iupac Common Name Chembl Id Clinical Phase Atoms Charge Curation Visibility. C 9 H 11 N O 2.
C 9 H 10 N O 2. - 22 -1. Post Lab Questions 1 Interpret the infrared and NMR spectra of benzocaine Sol from CHEM 101A-8 at Ohlone College.
Particulate-phase benzocaine will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Benzocaine is susceptible to direct photolysis as indicated by formation of this compound from photodegradation of ethyl N-phenyl-carbamate and further degradation of benzocaine to azo and colored products. If released to soil benzocaine is expected to have moderate mobility based upon.
There are a total of 11 protons on the NMR spectrum that can be explained by benzocaine indicating a gain in protons p-aminobenzoic acid would have a total of 7 protons present. Both the NMR and IR analysis indicated the synthesis of benzocaine was successful but it could not confirm the perfect isolation of benzocaine from impurities. The two impurities present in the compound tested was.
Benzocaine is a surface anesthetic that acts by preventing transmission of impulses along nerve fibers and at nerve endings. Benzocaine is a local anesthetic commonly used as a topical pain reliever. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter analgesic ointments.
Benzocaine is an ester a compound made from the organic acid PABA para. Benzocain ist ein Lokalanästhetikum vom Ester-Typ das vor allem in der Behandlung von Schmerzen eingesetzt wird. Im Gegensatz zu den meisten.
View the Full Spectrum for FREE. The full spectrum can only be viewed using a FREE account.