Convection currents can be seen in lava lamps. The formation of sea and land breeze form the classic examples of convection.

The warm air becomes cooler which causes moisture called water vapor to form small water droplets - a process called condensation.
How do convection cells form. Convection that occurs naturally is called natural convection or free convection. If a fluid is circulated using a fan or a pump its called forced convection. The cell formed by convection currents is called a convection cell or Bénard cell.
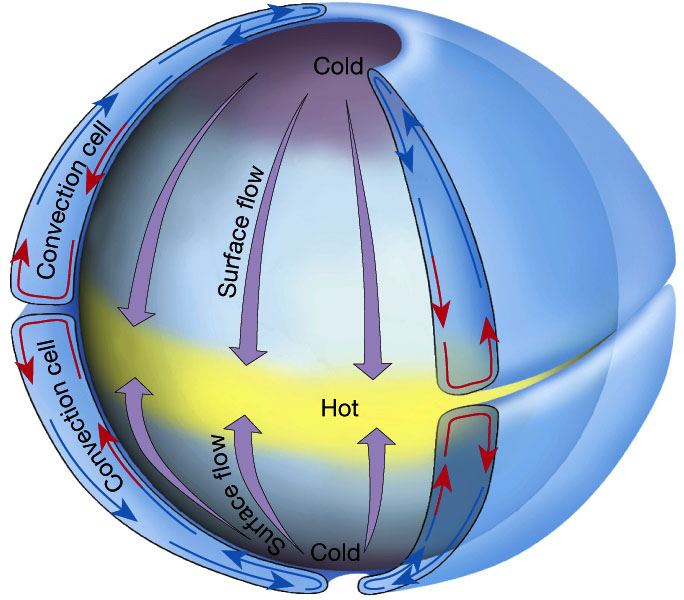
Convective cell The pattern formed in a fluid when local warming causes part of the fluid to rise and local cooling causes it to sink again elsewhere. The atmosphere in low latitudes forms such cells known as Hadley cells as warm equatorial air rises moves away from the equator and cools and then descends over the subtropics. Convection patterns in the molten zone for rotating or counter-rotating rods are very complicated.
To explain them the existence of upper and lower convection cells has been suggested. A schematic explanation of convection flows in the molten zone and their influence by rotation is shown in Figure 815. Because the flows on the convection.
Plates at our planets surface move because of the intense heat in the Earths core that causes molten rock in the mantle layer to move. It moves in a pattern called a convection cell that forms when warm material rises cools and eventually sink down. As the cooled material sinks down it is warmed and rises again.
How do convection cells work. At the top and right of the pot the water isnt as warm. This is because it doesnt have a source of heat altering its.
When hot water rises up it will try to go into an equilibrium. So at first that means that it mixes into the cold. Convection occurs when the Earth is heated unevenly.
The air over the Earth will heat according to how fast the Earth under it heats. That part of the atmosphere that heats faster will expand. This relationship between heat and volume is Charles Law.
The formation of sea and land breeze form the classic examples of convection. Going by the definition of convection the molecules at a higher temperature displace the ones at a lower temperature. Similarly in the afternoon the surface of the land near the sea is warmer as compared to in the evening.
The Earths big convection cells are either moving area upward in the atmosphere which tends to produce areas of low pressure and ofter rain and areas of descending air that gets compressed heated up and therefore is higher in pressure. The big series of Low pressures along the equator produces the tropical biome while the band of High pressure around 30S and 30N produce dry. Convection convection cell density global conveyor belt mantle mid-ocean ridge subduction zone vector viscosity Prior Knowledge Questions Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo You place a pot of soup on the stove.
As the soup warms you notice some areas where soup is rising up and other areas where soup is sinking. The first cell is called the Hadley cell. At the equator the ground is intensely heated by the sun.
This causes the air to rise which creates a low-pressure zone on the Earths surface. Convection is the transfer of heat by movement of a fluid such as air. Convection happens in the atmosphere when air near the Earths surface is heated.
This heating causes the air to expand become less dense than the surrounding air and rise. The heated air is. At this latitude air sinks and then to close the loop it returns to the equator along the surface.
Therefore because of the conservation of angularmomentum Hadley Cells exist only from the equator to the mid-latitudes. To conserve angular momentum velocity must increase as the radius decreases. Thunderstorms form when warm moist air rises into cold air.
The warm air becomes cooler which causes moisture called water vapor to form small water droplets - a process called condensation. The cooled air drops lower in the atmosphere warms and rises again. This circuit of rising and falling air is called a convection cell.
This lofted cool air travels east across the Pacific until it sinks pushing air on the surface back to the west and completing the cycle forming a convection cell. How Convection Works. Convection currents form because a heated fluid expands becoming less dense.
The less-dense heated fluid rises away from the heat source. As it rises it pulls cooler fluid down to replace it. This fluid in turn is heated rises and pulls down more cool fluid.
Convection currents can be seen in lava lamps. The wax inside the lamp warms up becomes less dense than the liquid and so rises. When it rises it cools and becomes denser again so it sinks.