The possibility that the underlying disease or other chemo-. The safety and efficacy of this three-drug regimen is unknown.
90 of patients with radiographical presence of honeycombing were non-responders.
High dose prednisone for pulmonary fibrosis. Pulmonary fibrosis2 A survey of pulmonologists showed that almost 50 used a regimen of either two drugs azathioprine plus prednisone or three drugs azathioprine prednisone and N-acetylcys-. Therapy with acetylcysteine at a dose of 600 mg three times daily added to prednisone and azathioprine preserves vital capacity and DL CO in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis better. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPF is a progressive fatal disorder in which chronic accumulation of neutrophils within the alveolar structures occurs.
These cells with their large stores of preformed mediators likely play a major role in subsequent lung derangement. To evaluate the adjunctive use of intermittent high dose pulse corticosteroid therapy as a means of inhibiting neutrophil accumulation in the IPF lung 5 patients were treated in a single blind random fashion with high dose. The clinical course of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPF is variable.
However the long-term survival in IPF is poor. Prednisone has been the mainstay of therapy since its release for clinical use in 1948. Recently prednisone combined with azathioprine or cyclophosphamide has been used.
A number of other drug combinations have been tried with prednisone eg methotrexate colchicine. Pulmonary textbooks all recommend corticosteroids for IPF4-9 and current practice mirrors these recom mendations. A survey of pulmonologists conducted by Smith and Moser10 in 1989 indicated that prednisone was the preferred therapy by 18 of the 25 respondents although criteria for.
The majority of prednisone-treated posIPF patients were non-responders 68 with a decrease in FVC 5 or death within 6 months from baseline. 90 of patients with radiographical presence of honeycombing were non-responders. In contrast six out of seven patients with focal desquamative interstitial pneumonia-like reaction in the SLB who had stopped smoking for 7.
Answers 1 For pulmonary fibrosis medications such as corticosteroids such as prednisone and cytotoxic drugs may help reduce swelling inflammation. -Dose of 1 mgkgday appears to be equally efficacious and may result in fewer behavioral side effects Maximum dose. 60 mgday Duration of therapy.
3 to 10 days Age. 12 years or older. 40 to 80 mg orally once a day or in 2.
Two patients treated for chronic myeloid leukemia with high doses of CCNU 1100 mgm2 and 1240 mgm2 respectively developed a fatal pulmonary fibrosis. This side effect has never been reported for this nitrosourea but only for BCNU and methyl-CCNU. The responsibility of CCNU in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis seems very likely.
The possibility that the underlying disease or other chemo-. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPF also called cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is specific form of chronic progressive fibrosing interstitial pneumonia of unknown cause occurring in adults and limited to the lungs. It is associated with the histopathologic andor radiologic pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia UIP.
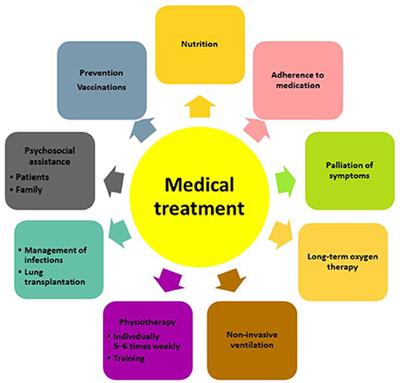
In the past treatment was aimed at minimizing inflammation and slowing the progression from inflammation to fibrosis. A combination of prednisone azathioprine and N-acetylcysteine NAC has been widely used as a treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The safety and efficacy of this three-drug regimen is unknown.
In this randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial we assigned patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulmonary exacerbations in patients with cystic fibrosis CF would result in a more rapid and greater increase in lung function. CF patients with an acute pulmonary exacerbation were randomized to receive oral placebo or prednisone 2 mgkgd up to 60 mg on days 1 to 5 in addition to standard therapy.
Colchicine appears to be a safer alternative to a trial of high-dose prednisone but may be no different than no therapy. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPF also known in the United Kingdom as cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is a group of disorders of unknown cause characterized by proliferation of excessive fibrous tissue in the lung. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic progressive disorder with a poor prognosis.
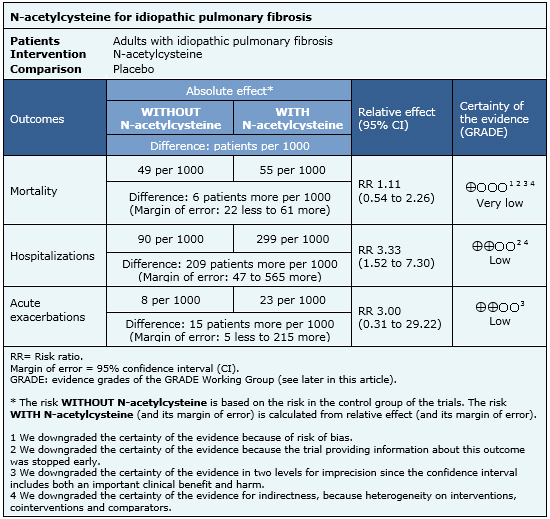
METHODS We conducted a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled multicenter study that assessed the effectiveness over one year of a high oral dose of acetylcysteine 600 mg three times daily added to standard therapy with prednisone plus azathioprine. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network Raghu G Anstrom KJ King TE Jr Lasky JA Martinez FJ. Prednisone azathioprine and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis.
It has been reported that cyclosporine A CYA treatment may benefit idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPF patients. We conducted a randomized controlled trial at 27 centers across Japan to evaluate the efficacy and safety of CYA with low-dose corticosteroids CS for IPF treatment. We compared these findings with others obtained using cyclophosphamide CPA combined with low-dose.
He was maintained on a steroid dosage of 40 mg of oral prednisone per day for 10 weeks in view of the pulmonary fibrosis on imaging. He was then transitioned to 20 mg for four weeks. Currently the patient is on 10 mg prednisone daily.
BACKGROUND Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic progressive disorder with a poor prognosis. METHODS We conducted a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled multicenter study that assessed the effectiveness over one year of a high oral dose of acetylcysteine 600 mg three times daily added to standard therapy with prednisone plus azathioprine. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic progressive disorder with a poor prognosis.
We conducted a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled multicenter study that assessed the effectiveness over one year of a high oral dose of acetylcysteine 600 mg three times daily added to standard therapy with prednisone plus azathioprine.