Calculating require SCFM for a jet mill. Use this calculator to determine the flow rate of any nozzle at any operating pressure.
Nozzle Outlet Velocity Equation.
Air nozzle velocity calculation. For a large container with a small orifice or hole from which the air escapes the velocity of escape theoretical may be calculated from the formula. V 2 Velocity of escaping air in feet per second ftsec. G Acceleration due to gravity 3216 feet per second squared 3216 ftsec 2.
If the pressure is coming from an air tank of finite volume this velocity is just a snapshot in time. The pressure and therefore velocity will decrease over time. We can approximate the pressure remaining after a tiny time interval by multiplying the mass flow rate by the time interval to get the air mass lost during the time interval determine the new density as mass divided by volume and thereby determine a new pressure.
The calculator is not for pulsating flow or non-steady flow when the flow rate is changing in time. This calculator also calculates total pressure drop created by the nozzle. You can use this calculator for all three types of nozzles covered in standards.
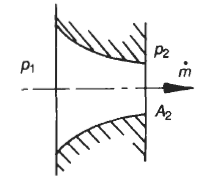
ISA 1932 nozzle long radius nozzle and Venturi nozzle. Velocity in a Nozzle. For unit mass The steady flow equation is q w Δ h Δ PE Δ KE.
For a horizontal nozzle Δ PE 0. There is no work-done in nozzle therefore W 0. In the nozzle the velocity of the fluid is so high that there is hardly any time available for fluid to exchange heat with the surroundings.
Therefore for nozzle it is assumed that heat transfer is zero ie flow in Isentropic. Example - Air Nozzles and Critical Pressure Ratios. The critical pressure ratio for an air nozzle can be calculated as.
P c p 1 2 14 1 14 14 - 1 0528. Critical pressures for other values of - n. Used to calculate the amount of air that will pass through the nozzles of a jet mill in SCFM for compressor sizing.
Calculating require SCFM for a jet mill. Use this calculator to determine the flow rate of any nozzle at any operating pressure. Inputs to this calculator are the nozzle type current operating pressure and flow desired flow or desired pressure.
By multiplying air velocity by the cross section area of a duct you can determine the air volume flowing past a point in the duct per unit of time. Volume flow is usually measured in Cubic Feet per Minute CFM. Concept of Air Velocity can be used in air conditioning heating and ventilating work.
Online calculator to quickly determine Air Flow Rate through an Orifice. Includes 53 different calculations. Equations displayed for easy reference.
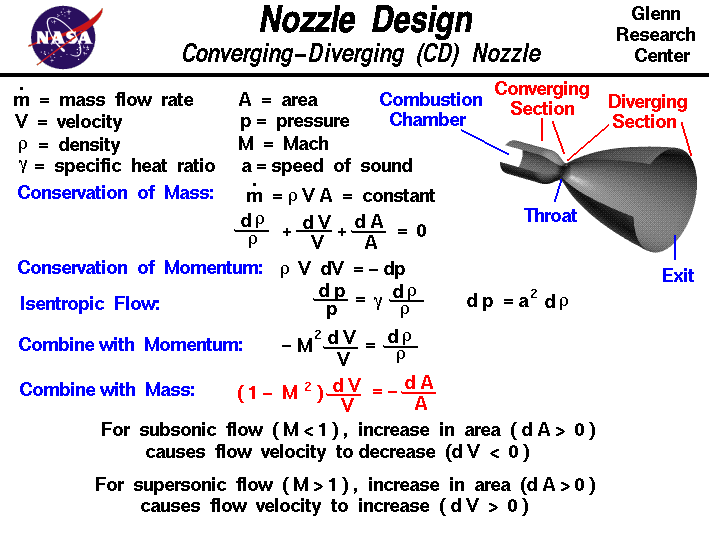
Nozzle Outlet Velocity Equation. Note that C 2 is independent of p 2 and that the nozzle flow is a maximum. In this case the nozzle is said to be choked.
P 1 Inlet pressure N m 2 Pa p 2 Outlet pressure N m 2 Pa p c critical pressure at throat N m 2 Pa v 1 Inlet specific volume m 3 v c Outlet specific volume m 3 C 2 Outlet velocity msec C c Throat velocity msec. For orifices and nozzles installed in horizontal pipework where it can be assumed that there is no elevation change head loss and flow rate may be calculated as follows. Vertical Orifices and Nozzles For orifices and nozzles installed in vertical piping with elevation change Delta z z_ 1 - z_ 2 Δz z 1.
Determine how far the air can be projected and the velocity decay characteristics of the air stream. 1 air volume or mass of air flow 2 discharge velocity or nozzle velocity and 3 outlet configuration. AIR VOLUME In general the larger the air volume or air mass the further it can be projected.
A projectile in excess of 100 pounds from a 16. Air at 78 bar and 180 0C expands through a convergent divergent nozzle into a space at 103 bar. The flow rate of air is 36 kgs.
Assuming isentropic flow throughout and neglecting the inlet velocity calculate the throat and exit areas of the nozzle. 3D plot of the equation for mass flow rate of gas as function the inlet pressurea and the back-pressure is called flow rate cone of the nozzle. Problem 102 The air flows through a nozzle its velocity is 250 ms-1 its pressure is 1 MPa its temperature is 350 C at the inlet of the nozzle.
Surroundings pressure behind the nozzle is 025 MPa. There are many people who believe that water jet has higher pressure which is coming out of nozzle. They believe that pressure is inversely proportional to a.
Venturi nozzle calculation according to the Bernoullis Theorem The Bernoulli equation can be considered as a principle of conservation of energy suitable for moving fluidsThe behavior usually called Venturi effect or Bernoulli effect is the reduction of fluid. Calculates the needed diameter of a nozzle for a specific pressure and flow rate. Psi ft of water m of water bars kPa atm in of Mercury.
Gpm lps cfs lpm. In 128ths in 64ths in 32nds in 16ths in 8ths in mm cm. Solving for velocity.
W1 v C v 2 G H p ρ where v velocity of the water from the nozzle C v the velocity coefficient 097 for water G the total acceleration g a where.